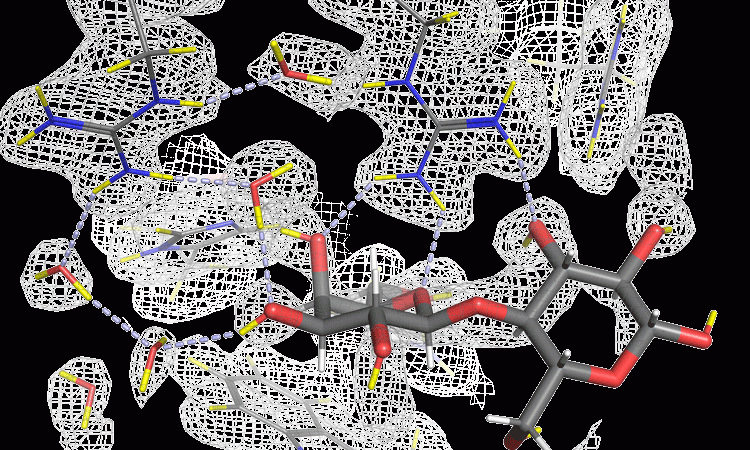
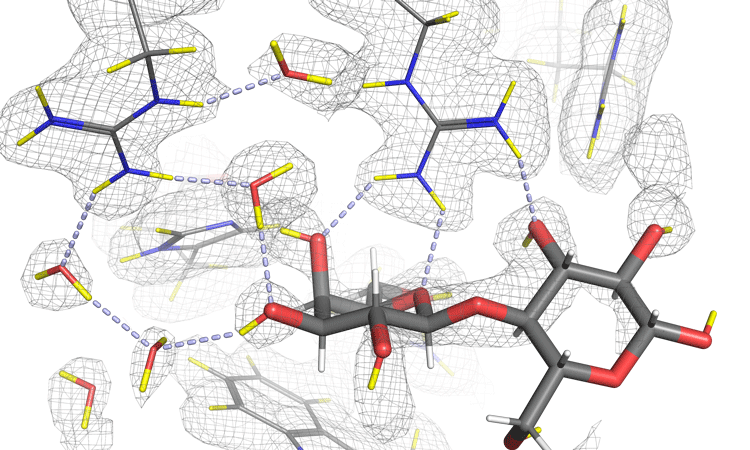
Encouraging drug discovery and therapeutic targets for dementia
A review has been published by experts in neurodegeneration research, detailing six ways to improve dementia research. This article investigates one of these suggestions, focusing on how we can improve drug target identification.