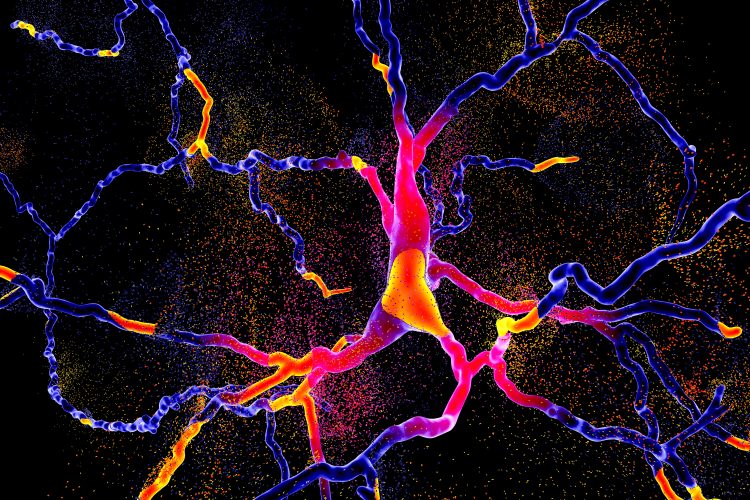
A novel blood-brain barrier model for cerebral malaria research
In this article Maria Bernabeu, Group Leader at EMBL, Barcelona, discusses why it is important to research and develop novel therapeutics for cerebral malaria and how her research group intends to develop a 3D blood-brain barrier model for this purpose.