ComFB protein discovery could help fight antibiotic resistance
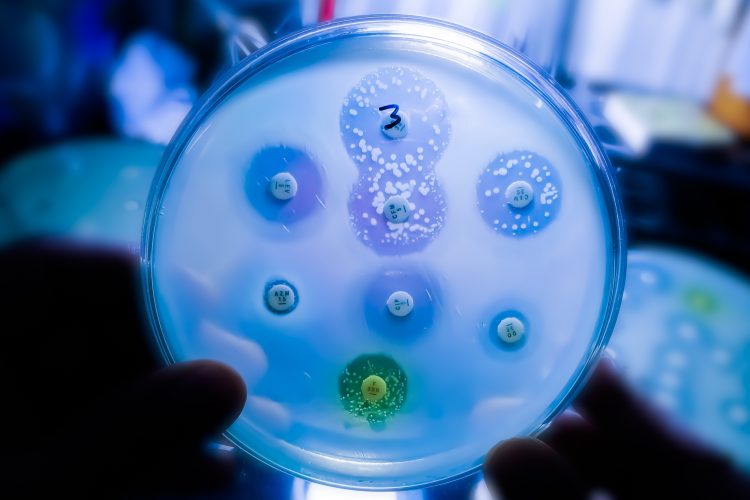
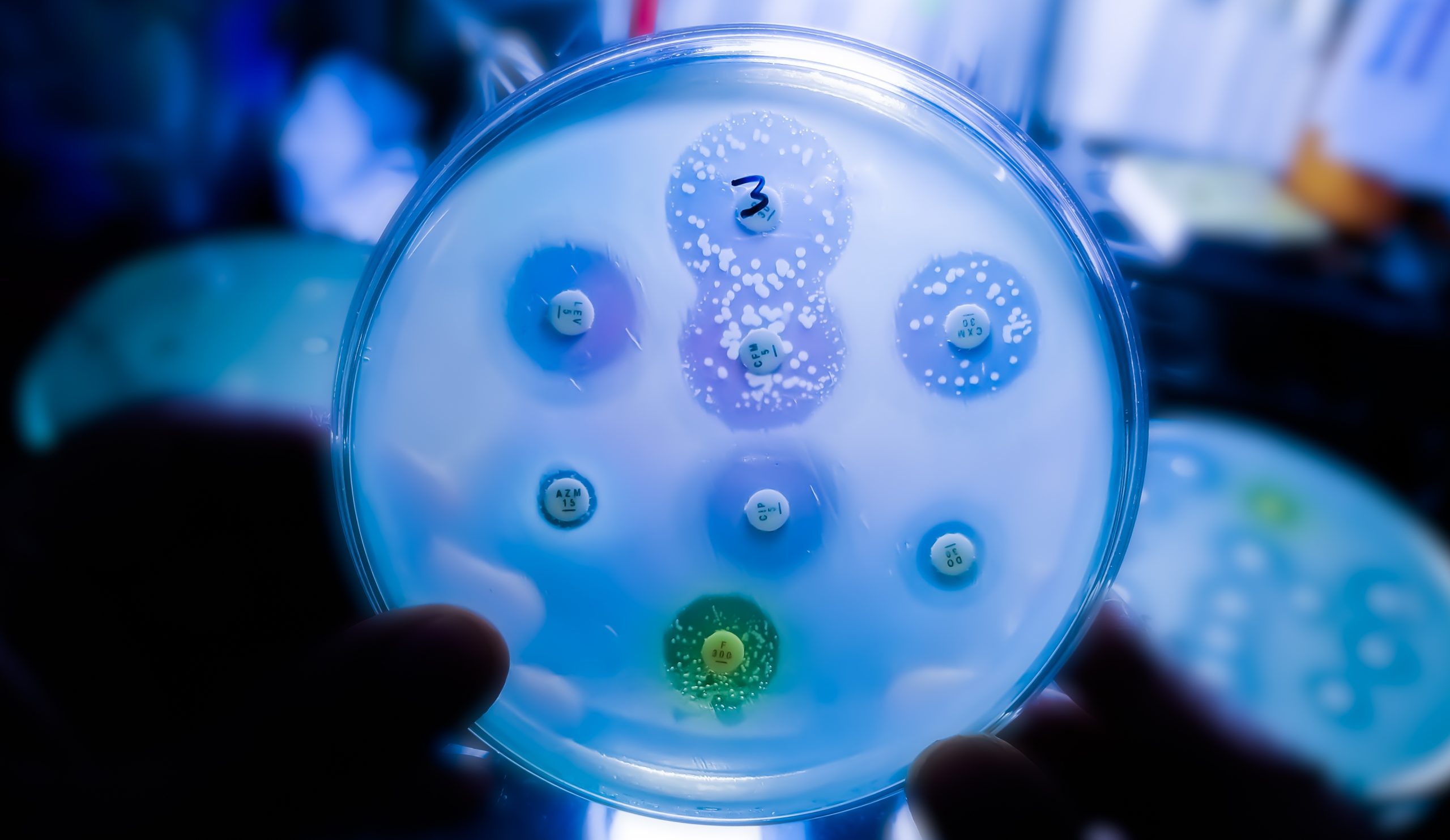
Scientists have discovered a new family of bacterial proteins – called ComFB – that regulate both movement and DNA uptake – suggesting potential new methods to combat pathogenic infections.







![Wasp on a wooden platform [Credit: University of Pennsylvania].](https://www.drugtargetreview.com/wp-content/uploads/Vespula-lewisii-wasp-750x500.jpg)
![Wasp on a wooden platform [Credit: University of Pennsylvania].](https://www.drugtargetreview.com/wp-content/uploads/Vespula-lewisii-wasp-e1602594547599.jpg)