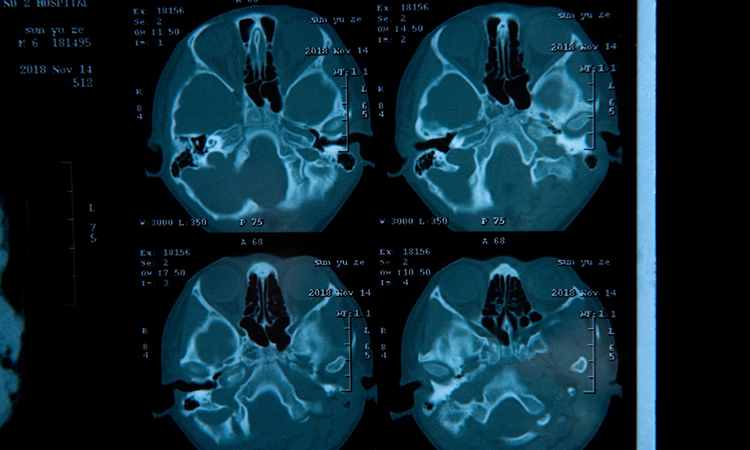
Stem cell replacement therapy: a potential treatment for Parkinson’s disease
In a new study, researchers describe a process for converting non-neuronal cells into functioning neurons able to restore capacities undermined by Parkinson’s destruction of dopaminergic cells.