Study aims to stop Alzheimer’s with stem cell infusions
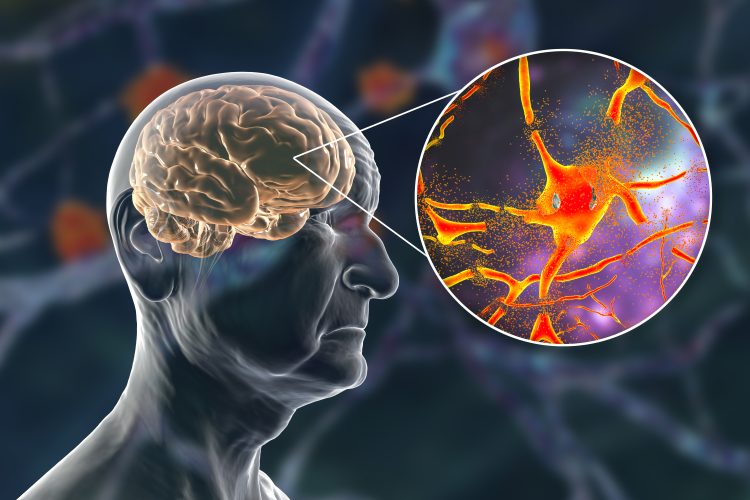
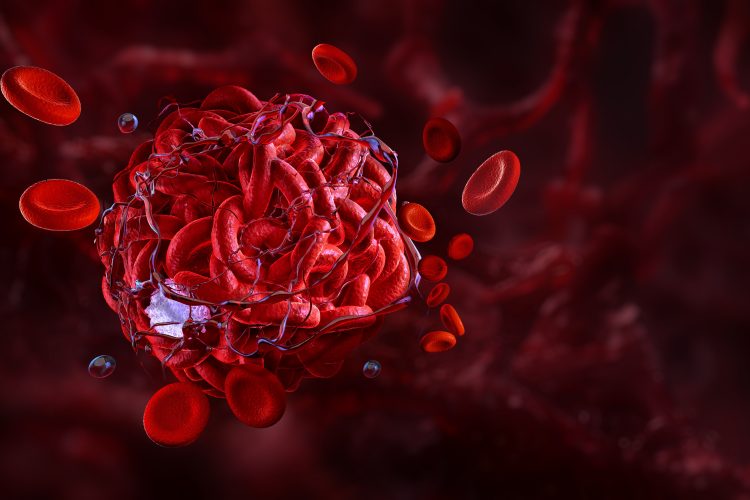
Researchers at UTHealth Houston have initiated a new stem cell therapy trial aimed at reducing neuroinflammation to prevent Alzheimer's disease before symptoms emerge, an approach that could revolutionise treatment strategies, offering new hope for at-risk individuals.