Using immunotherapy to prevent cancer metastases
Posted: 13 June 2022 | Ria Kakkad (Drug Target Review) | No comments yet
Scientists have demonstrated how killer T cells used in immunotherapy to eliminate cancer cells can also destroy tumour lymphatic vessels, thus greatly reducing the risk of metastasis.

To grow, tumours rely on a specific structure, the tumour stroma. This includes blood vessels, which provide the nutrients necessary for the multiplication of diseased cells, and of lymphatic vessels, through which they migrate to metastasise. The development of lymphatic vessels — a mechanism known as lymphangiogenesis — in and around a tumour is therefore of poor prognosis. A team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), Switzerland, has demonstrated how killer T cells used in immunotherapy to eliminate cancer cells can also destroy tumour lymphatic vessels, thus greatly reducing the risk of metastasis. Exploiting this synergistic effect could increase the effectiveness of treatments against cancers where lymphangiogenesis is important, such as colorectal cancer, melanoma, or breast cancer. These results were recently published in Science Advances.
The lymphatic system is the main route through which cancer cells spread in the body. They first colonise the sentinel lymph nodes, then move to give rise to secondary metastases elsewhere in the body. However, therapies to block tumour lymphangiogenesis have so far been disappointing.
“Indeed, they also represent the route for some immune cells, the dendritic cells, to exit from the tumor and activate anti-tumoral killer T cells,” explained Associate Professor Stéphanie Hugues, who led this work. “We must therefore find a balance in order to inhibit this mechanism without blocking it completely, and thus decipher its mode of action in detail”.
To do this, the scientists used killer T lymphocytes used in immunotherapy protocols. ‘‘These T-cells are immune cells specifically activated in labs to eliminate tumour cells, before being injected to patients,’’ explained Laure Garnier, the first author of this work. ‘‘Here, we injected them into mice suffering from melanoma. And if, as expected, the killer lymphocytes destroyed the tumour cells, they also attacked the lymphatic endothelial cells that line the lymphatic vessels.”
The destruction of cancer cells leads to the release of tumour antigens. These small cancerous parts are then captured by the lymphatic endothelial cells which, having become carriers of tumour identification markers, are also recognised as enemies by the T cells that attack them. This mechanism therefore disrupts the tumour-associated lymphatic system to significantly reduce the risk of metastasis without blocking it entirely.
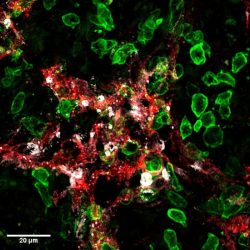

Killer-T cells (green) attack lymphatic vessels (red) in tumours and induce their death (cell death marker in white)
[Credit:
UNIGE – Robert Pick / Stéphanie Hugues].
The research team confirmed these results with other approaches, such as vaccination, which aims to strengthen the immune system. ‘‘We also observed the destruction of lymphatic endothelial cells, and consequently a decrease in lymph node metastases, thus limiting the risk of secondary metastases. Moreover, as this action only takes place in the tumour microenvironment, no systemic effect is to be feared,’’ emphasised Garnier.
There are several options to strengthen the effect without jeopardising the action of the immune cells, such as intervening once immunity has been established, or in conjunction with therapeutic protocols where the immune system is so strong that limiting lymphangiogenesis would not impair its function. ‘‘Nevertheless, our results show that the most effective approach is to use killer T-cells generated in the laboratory, and therefore ready to attack, in order to bypass the first phase of activation, which can prove problematic,’’ said Hugues.
Immunotherapies remain complex and are only used when traditional treatments have proved inconclusive. ‘‘Even though they are very promising, these therapies are not miracle solutions and often cause severe side effects. This is why we want to understand the smallest biological processes at work,” the authors concluded.
Related topics
Immuno-oncology, Immunotherapy, T cells
Related conditions
Breast cancer, Colorectal cancer, Melanoma
Related organisations
University of Geneva (UNIGE)
Related people
Associate Professor Stéphanie Hugues, Laure Garnier