3D map reveals DNA organisation within human retina cells
Posted: 25 October 2022 | Ria Kakkad (Drug Target Review) | No comments yet
Scientists shed light on how genetic architecture in human retina cells determine gene expression, tissue-specific function, and disease phenotype in blinding diseases.


In a new study from the US National Eye Institute (NEI), researchers mapped the organisation of human retinal cell chromatin, the fibres that package 3 billion nucleotide-long DNA molecules into compact structures that fit into chromosomes within each cell’s nucleus. The resulting comprehensive gene regulatory network provides insights into regulation of gene expression in general, and in retinal function, in both rare and common eye diseases. The findings were recently published in Nature Communications.
“This is the first detailed integration of retinal regulatory genome topology with genetic variants associated with age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and glaucoma, two leading causes of vision loss and blindness,” said the study’s lead investigator, Dr Anand Swaroop.
Adult human retinal cells are highly specialised sensory neurons that do not divide and are therefore relatively stable for exploring how the chromatin’s three-dimensional structure contributes to the expression of genetic information.
Chromatin fibres package long strands of DNA, which are spooled around histone proteins and then repeatedly looped to form highly compact structures. All those loops create multiple contact points where genetic sequences that code for proteins interact with gene regulatory sequences, such as super enhancers, promoters, and transcription factors.
Such non-coding sequences were long considered “junk DNA.” But more advanced studies demonstrate ways these sequences control which genes get transcribed and when, shedding light on the specific mechanisms by which non-coding regulatory elements exert control even when their location on a DNA strand is remote from the genes they regulate.
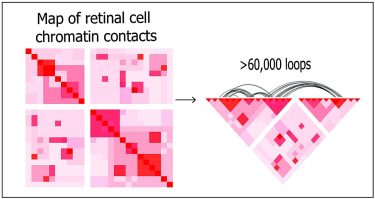

Using deep Hi-C sequencing, a tool used for studying 3D genome organisation, the researchers created a high-resolution map of retinal cell chromatin contract points, shown left. The entire map included about 704 million contact points. Shown right, more than 60,000 chromatin loops are represented on a portion of the map. [Credit: Dr Anand Swaroop, NEI].
Using deep Hi-C sequencing, a tool used for studying 3D genome organisation, the researchers created a high-resolution map that included 704 million contact points within retinal cell chromatin. Maps were constructed using post-mortem retinal samples from four human donors.
The researchers then integrated that chromatin topology map with datasets on retinal genes and regulatory elements. What emerged was a dynamic picture of interactions within chromatin over time, including gene activity hot spots and areas with varying degrees of insulation from other regions of DNA.
They found distinct patterns of interaction at retinal genes suggesting how chromatin’s 3D organisation plays an important role in tissue-specific gene regulation.
“Having such a high-resolution picture of genomic architecture will continue to provide insights into the genetic control of tissue-specific functions,” Swaroop said.
Furthermore, similarities between mice and human chromatin organisation suggest conservation across species, underscoring the relevance of chromatin organisational patterns for retinal gene regulation. The team found that 35.7 percent of gene pairs interacting through a chromatin loop in mice also did so in human retina.
The researchers integrated the chromatin topology map with data on genetic variants identified from genome-wide association studies for their involvement in AMD and glaucoma. The findings point to specific candidate causal genes involved in those diseases.
The integrated genome regulatory map will also assist in evaluating genes associated with other common retina-associated diseases such as diabetic retinopathy, determining missing heritability and understanding genotype-phenotype correlations in inherited retinal and macular diseases.
Related topics
Disease Research, Genomics, Protein
Related conditions
age-related macular degeneration (AMD), blindness, Glaucoma
Related organisations
US National Eye Institute (NEI)
Related people
Dr Anand Swaroop