Short chain fatty acid supplementation could improve stroke recovery
Posted: 3 January 2020 | Victoria Rees (Drug Target Review) | No comments yet
Researchers have found that supplementing drinking water with short chain fatty acids helped mice to recover from stroke by increasing microglia activity.

According to new research, supplementing the body’s short chain fatty acids in the microbiome could improve stroke recovery. The scientists behind the findings say that this supplementation may be a non-invasive addition to stroke rehabilitation therapies.
The researchers, part of the Society for Neuroscience, revealed that in mice, the gut microbiome influences brain health including how the brain recovers from stoke. Previously, short chain fatty acids, a fermentation product from gut bacteria and essential for gut health, have not been explored as a potential route for stroke recovery.
The researchers added the acids to the drinking water of mouse models for four weeks before inducing a stroke. The mice that drank the fatty acid water experienced a better stroke recovery compared to the control mice, including reduced motor impairment and increased spine growth on dendrites, a crucial memory structure.
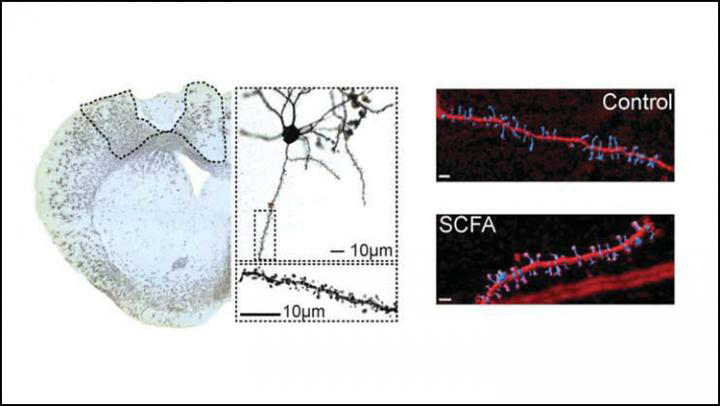

Post-stroke neuronal plasticity is altered by short-chain fatty acid treatment (credit: Sadler et al., JNeurosci 2019).
Additionally, the team found that fatty acid-supplemented mice expressed more genes related to microglia, the brain’s immune cells. The researchers suggest that microglial activity could be responsible for increasing dendritic spines and improving stroke outcome. This relationship indicates that short chain fatty acids may serve as messengers in the gut-brain connection by influencing how the brain responds to injury.
The study’s authors write that they “identified that this effect was mediated via circulating lymphocytes on microglial activation. These results identify short chain fatty acids as a missing link along the gut-brain axis and as a potential therapeutic to improve recovery after stroke.”
The results were published in JNeurosci.
Related topics
Drug Targets, Microbiome, microglial cells, Neurosciences, Therapeutics
Related conditions
Stroke
Related organisations
Society for Neuroscience