Macaques develop short-term immunity to SARS-CoV-2
Posted: 6 July 2020 | Hannah Balfour (Drug Target Review) | No comments yet
Researchers experimenting on macaques reveal they were protected against reinfection up to a month after the initial exposure to SARS-CoV-2.
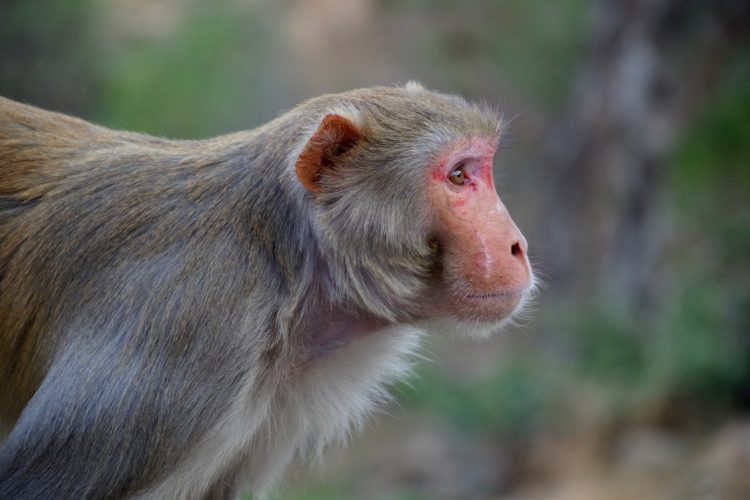


Six rhesus macaques infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus causing the COVID-19 pandemic, were protected from reinfection for up to 28 days later.
Scientists from Peking Union Medical College, China, performed the experiment to find out if infection by SARS-CoV-2 would provide non-human primates with short-term immunity to the virus.
Six macaques were infected with SARS-CoV-2 in their trachea, all developed mild to moderate symptoms which they recovered from after two weeks. A month later, four of the six monkeys received another dose of SARS-CoV-2.
While the macaques had a brief rise in temperature following the second exposure, they displayed no signs of reinfection, said the study authors.
Frequent samples were taken by researchers throughout the experiment. These allowed the team to identify that the peak viral load was reached three days after the monkeys were infected.
According to the paper, the macaques showed a stronger immune response after the first infection, producing more neutralising antibodies which may have protected them against short-term reinfection.
The researchers caution that more experiments are needed to establish how long this immunity remains and that it is still unclear how it will last in humans – the world will need to wait months or even years to know if the millions of people infected during the COVID-19 pandemic are protected from reinfection.
The paper was published in Science.
Related topics
Disease Research, Immunology, In Vivo
Related conditions
Coronavirus, Covid-19
Related organisations
Peking Union Medical College