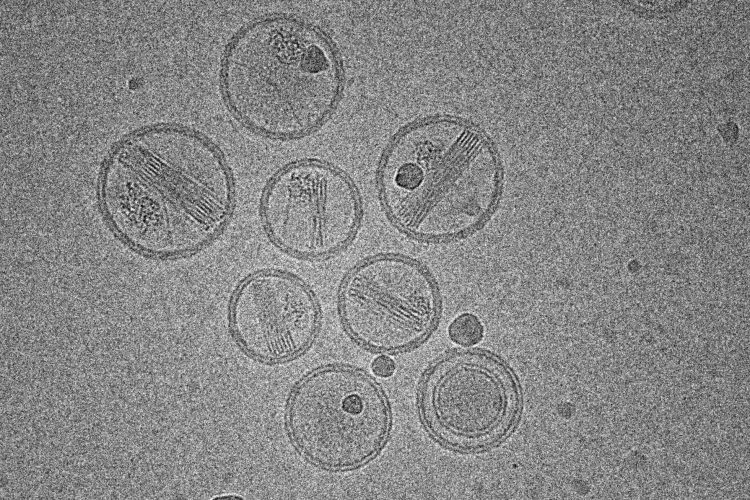
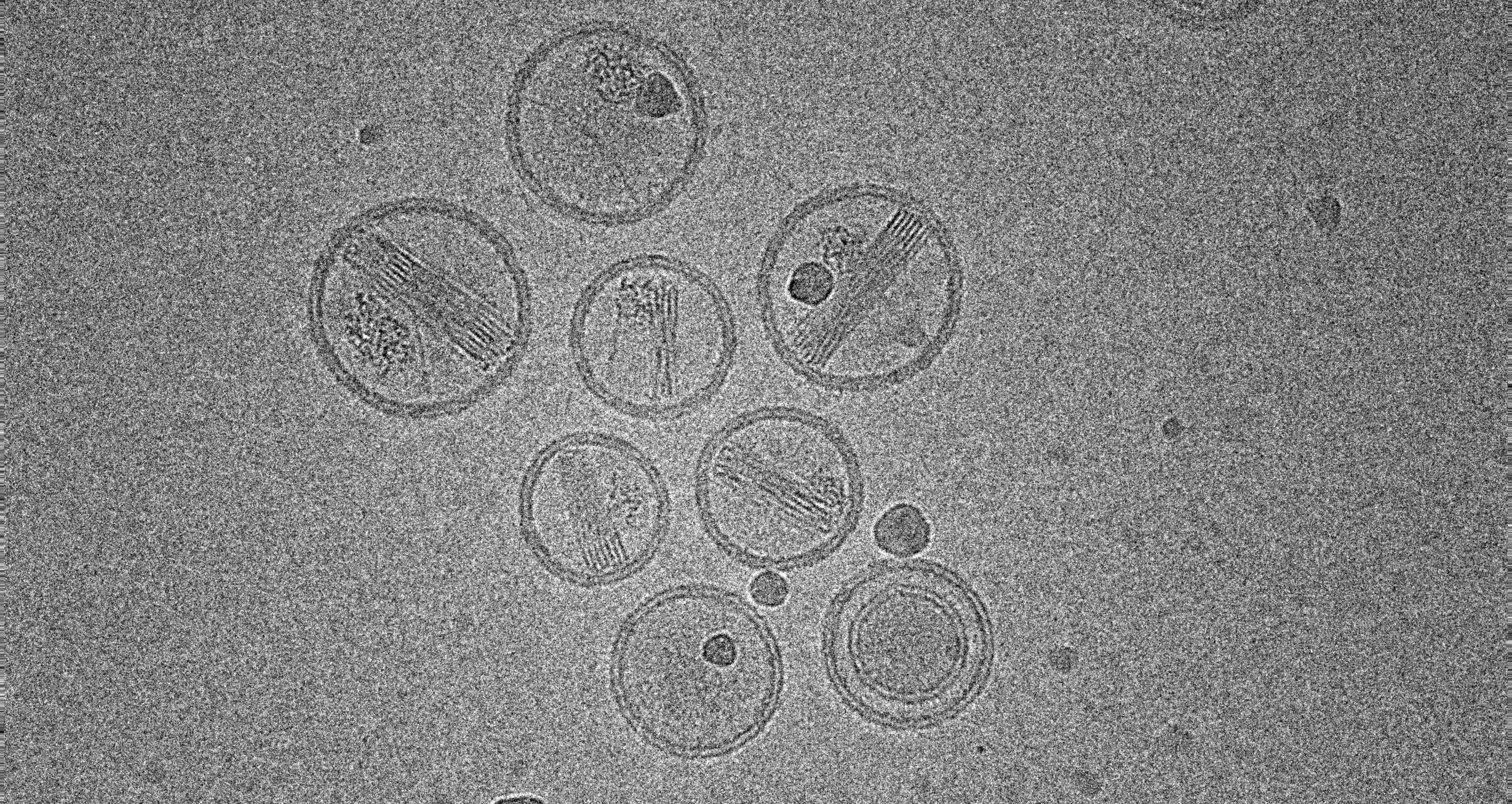
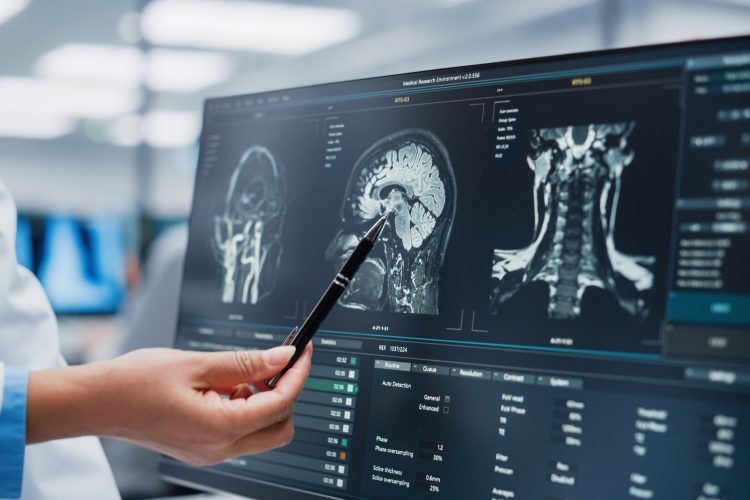
Turning up the heat: simple temperature change makes versatile vaccine nanoparticles
University of Chicago researchers have developed a scalable nanoparticle platform that self-assembles with just a temperature change – enabling safe, solvent-free delivery of proteins and RNA for vaccines and therapies.