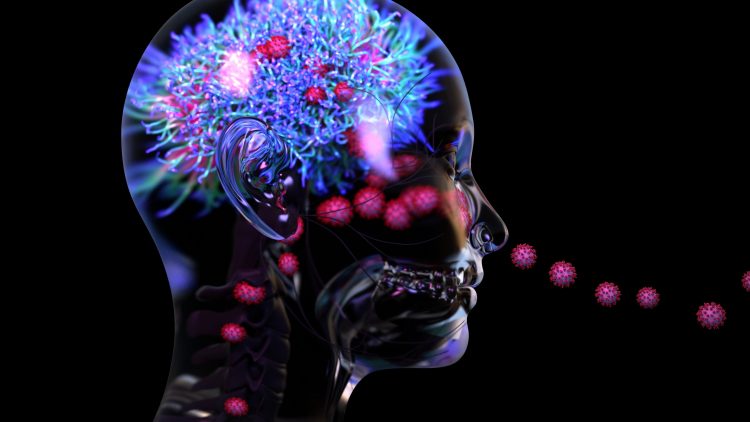
Blood vessel damage likely causes neurological symptoms of COVID-19, finds study
A new study suggests that inflammation and blood vessel damage may be the primary causes of neurological symptoms in COVID-19 patients, instead of the virus infecting the brain.