Ginger-based compound targets inflammation in IBD
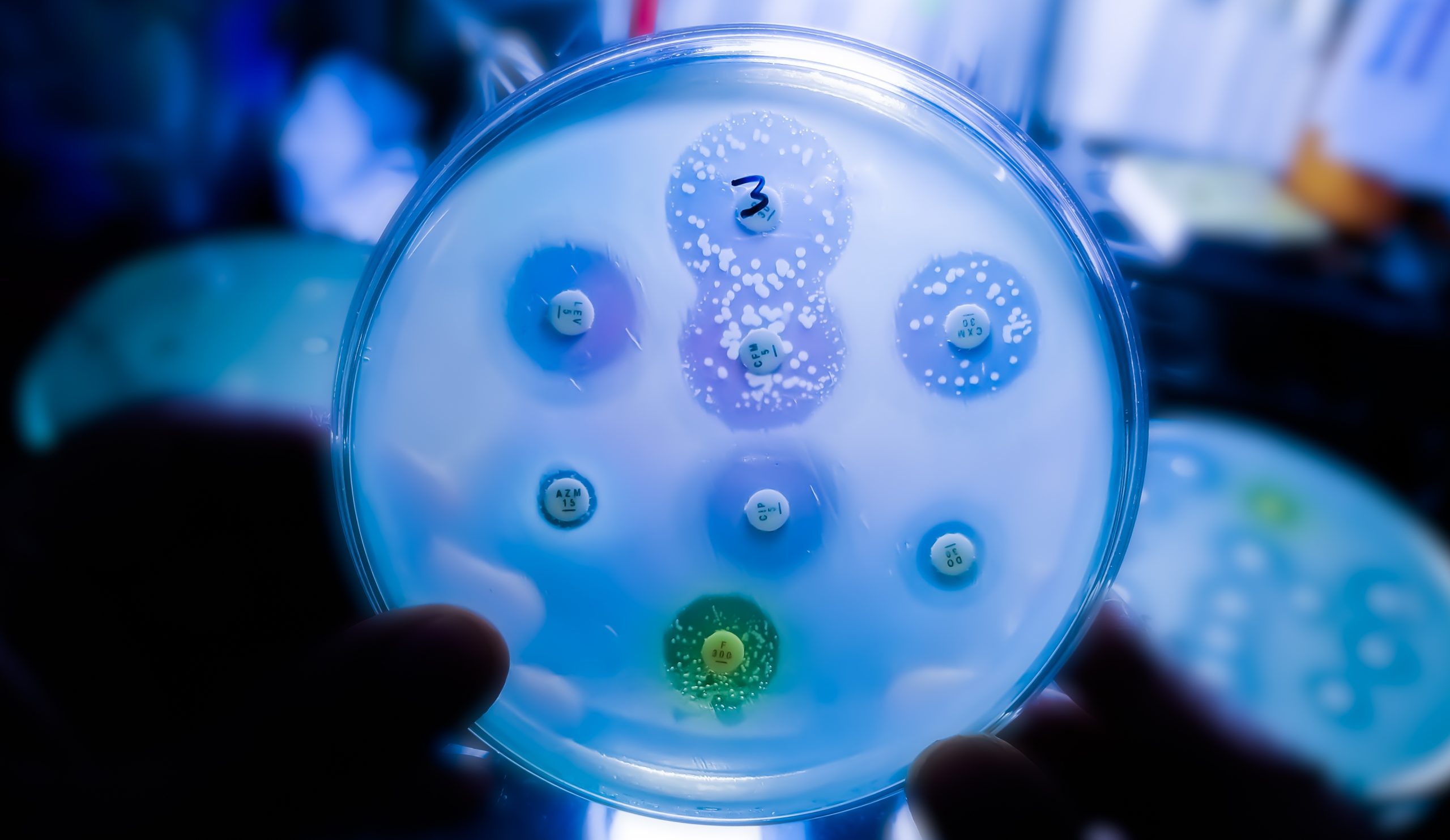
Researchers at the University of Toronto have discovered a compound in ginger, furanodienone (FDN), that interacts with the pregnane X receptor to reduce inflammation in the colon. This finding suggests FDN could be an effective, natural treatment for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).