Enhancing the speed of atomic force microscopy for biological samples
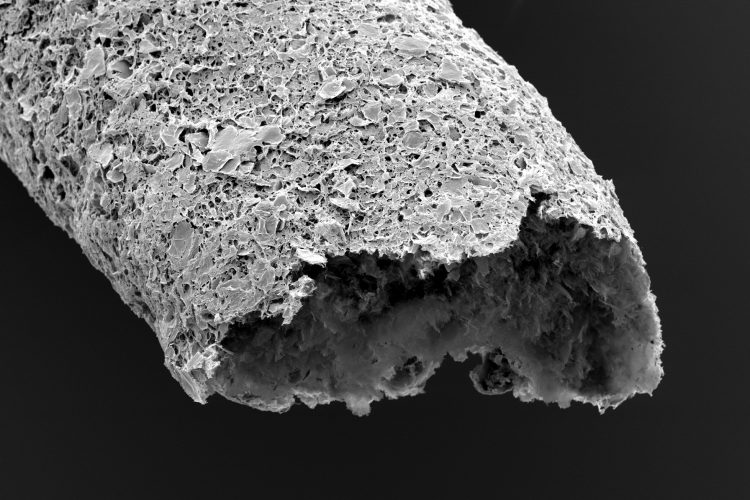
Researchers have applied for a patent for their innovative cantilever and vibrating plate technique which they say could increase the speed of atomic force microscopy on fragile samples.