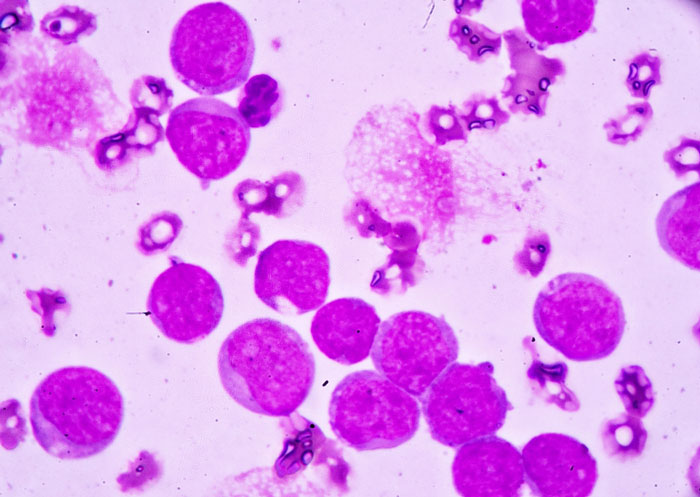
Modified PIP protein differentiates between cancerous and non-cancerous cells
A discovery sheds light on how cancerous cells differ from healthy ones and could lead to the development of new strategies for therapeutic intervention for difficult-to-treat cancers...