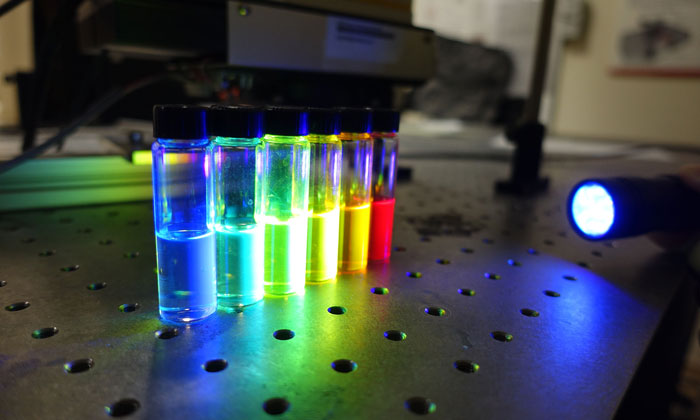
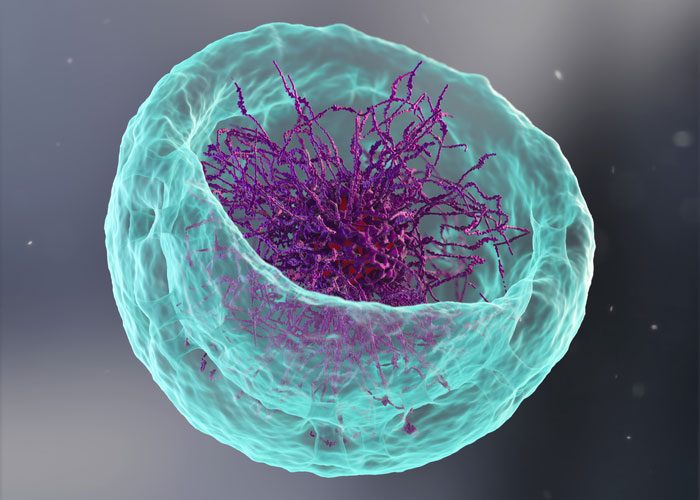
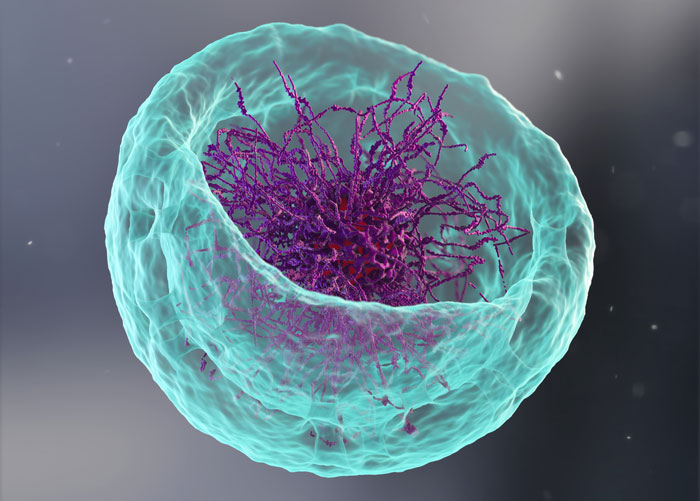
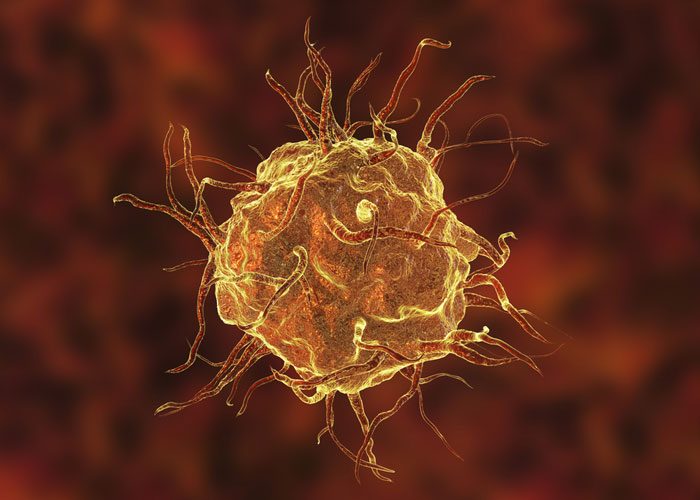
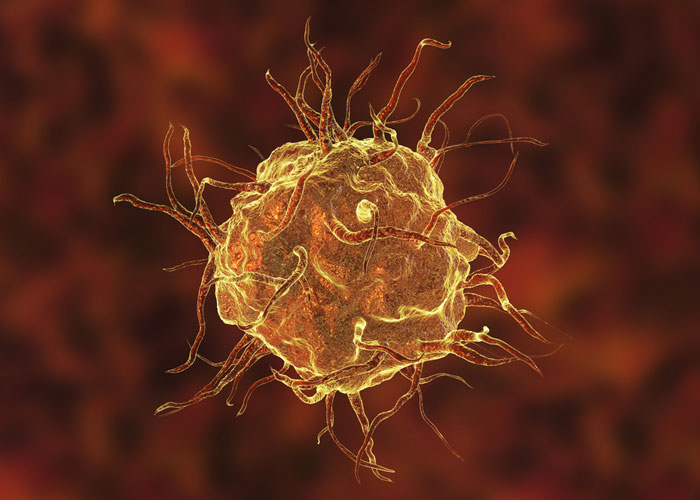
Scientists create “tracking” nanoagents to illuminate very small diseased tissues
Polymer nanoagents that can ‘light up’ tiny areas of diseased tissues that conventional methods fail to detect, have been created by a research team led by NTU Singapore.