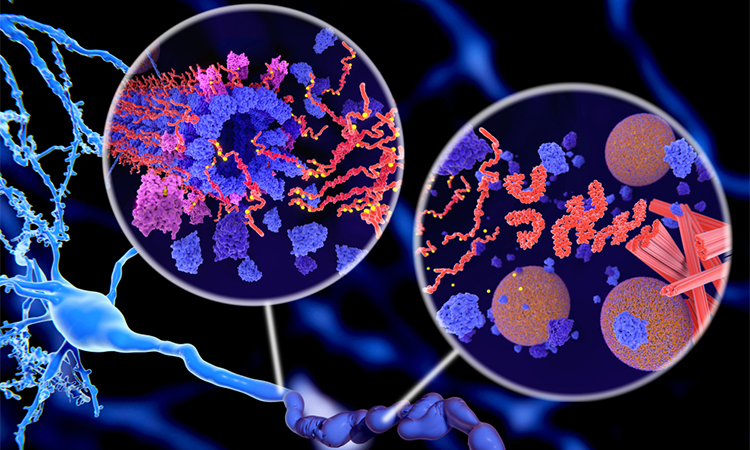
Advanced drug development for neurodegenerative diseases with α-synuclein
Discover how α-synuclein tests are transforming the diagnosis and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, offering hope for earlier detection, better-targeted therapies and faster drug development.