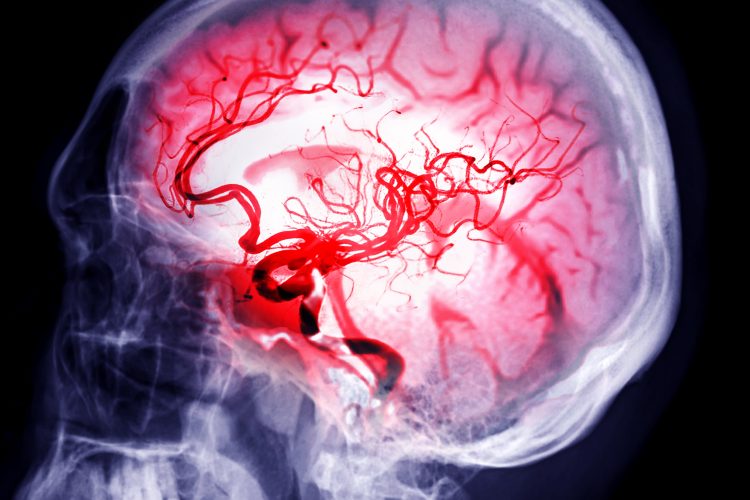
New stem cell approach could repair stroke-damaged brains
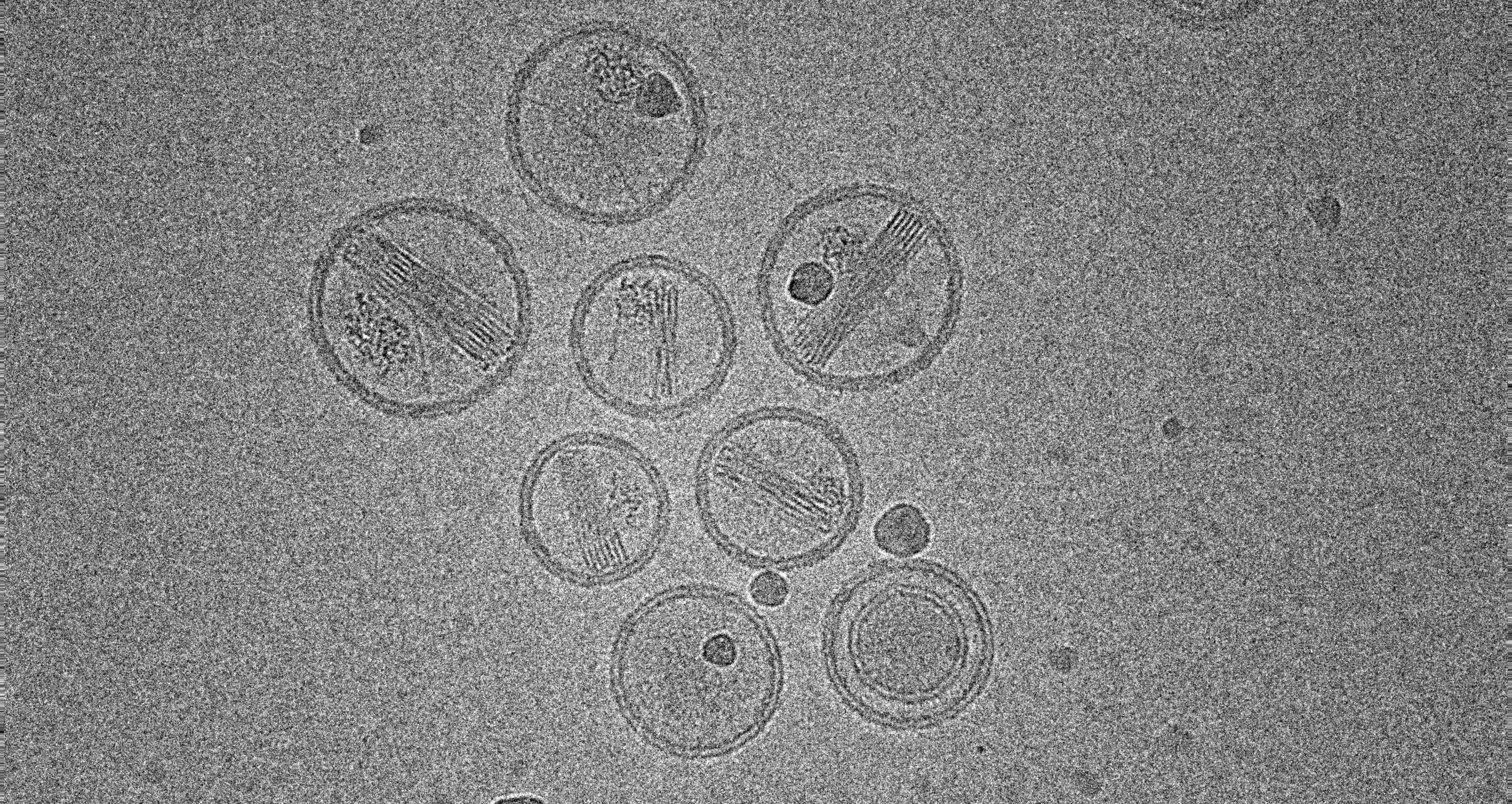
A new experimental stem cell therapy shows promise in repairing brain damage after ischemic strokes – potentially allowing for the development of future treatments that extend the recovery window.