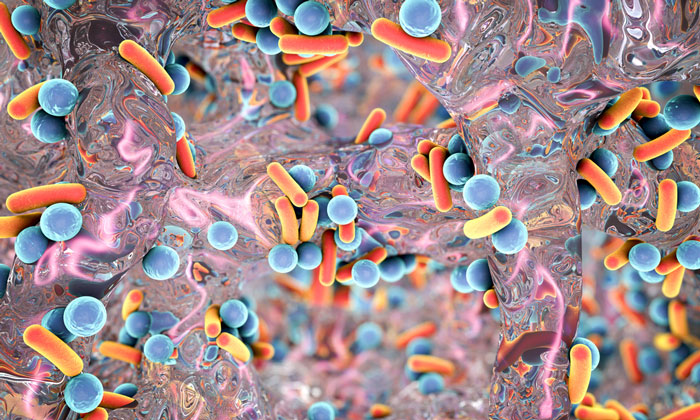
How medications in waterways are encouraging antibiotic resistance
New research has discovered that mixtures of everyday medications in the environment can promote antibiotic resistance, offering new insights that could influence future drug discovery and environmental policy.