How to develop the next generation of CAR T-cell therapies
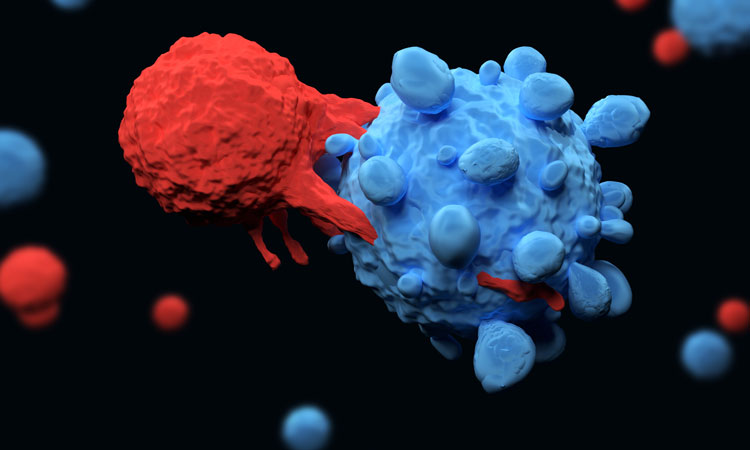
CAR T cells have shown incredible promise in the clinic, but there is still room for advancement. One avenue for improvement is through modification of the CAR design. However, given the number of exchangeable domains, testing all variations can present a hurdle. In this article, Dr Sarwish Rafiq, Assistant Professor in…