Researchers observe interaction between antibodies and target proteins
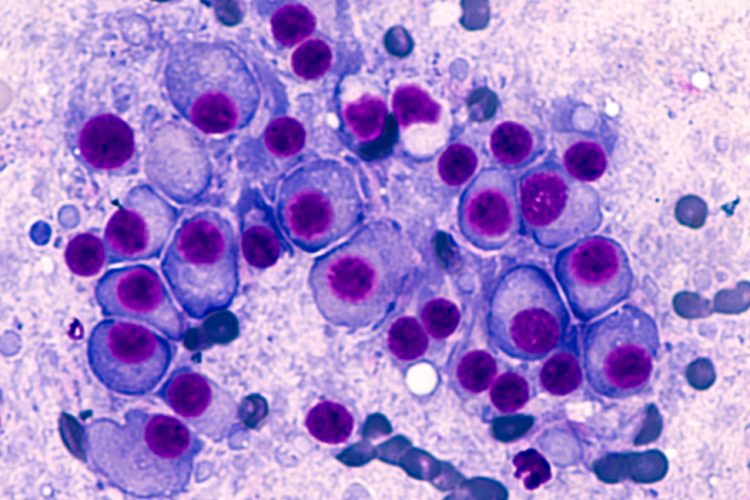
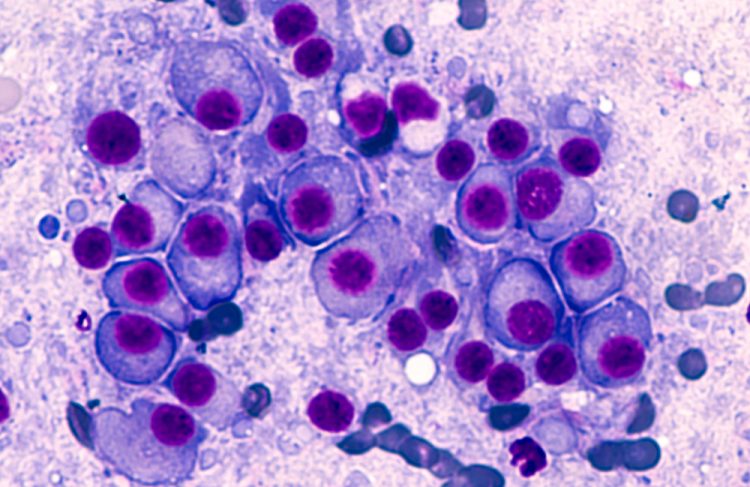
Using cryogenic electron microscopy, scientists have observed the interaction between antibodies and their target molecules, providing information that could be utilised in the development of synthetic antibodies.