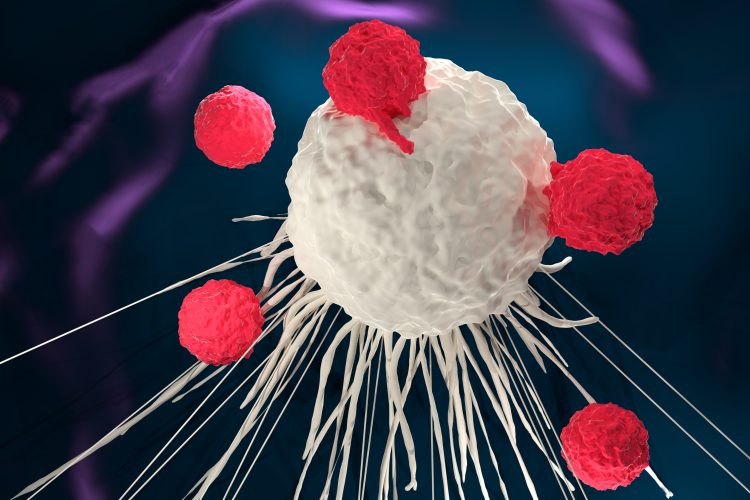
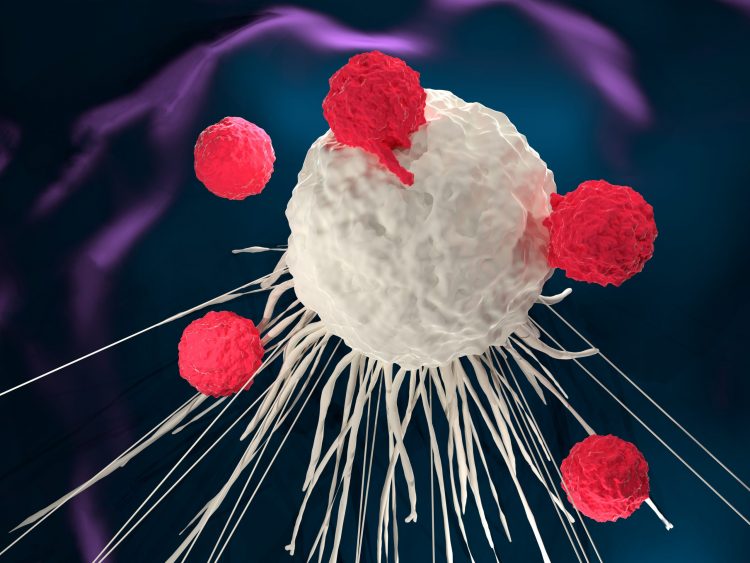
Researchers find VISTA molecule silences immune system against cancer
A new study shows that the VISTA molecule stops the immune system responding to self-antigens, including those presented by cancer cells, so an anti-VISTA antibody could be a possible therapy.