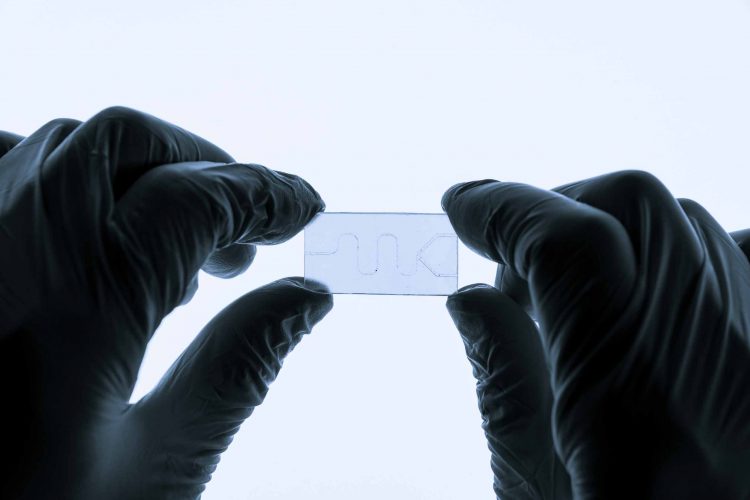
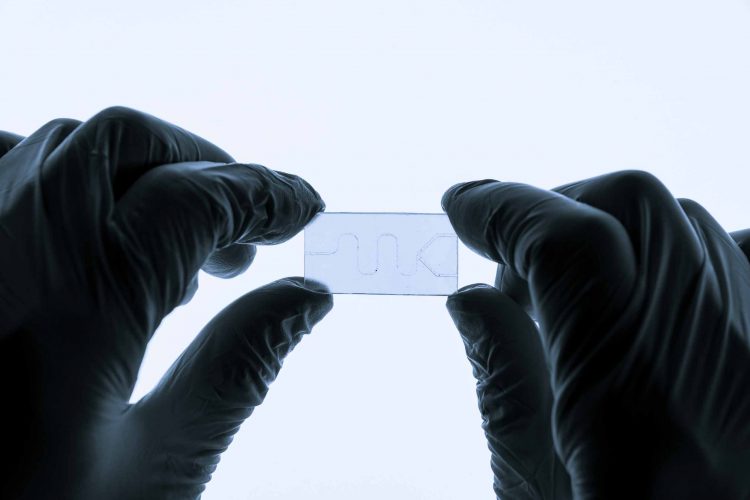
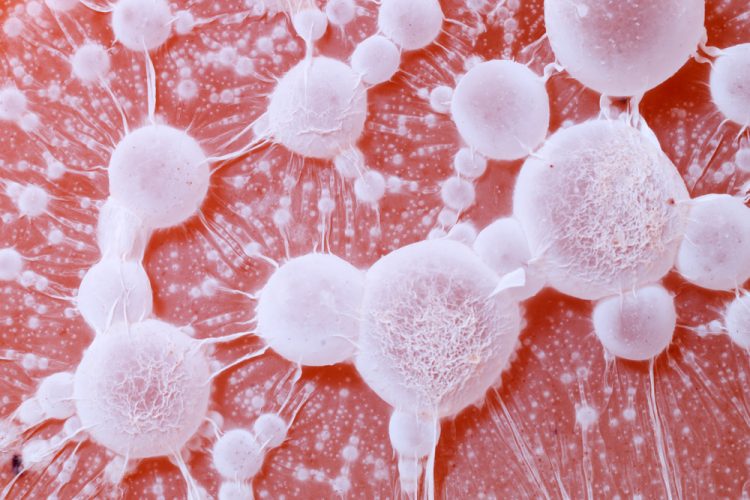
High-throughput 3D cell migration assays in organ-on-a-chip technologies
Organ-on-a-chip models can provide an alternative to cell cultures, animal models and traditional assays. In this article, Dr Désirée Goubert, Thomas Olivier, Luuk de Haan and Dr Lenie van den Broek explore the advantages of organ-on-a-chip technologies and how they can enable the in vitro study of three-dimensional (3D) cell migration in…