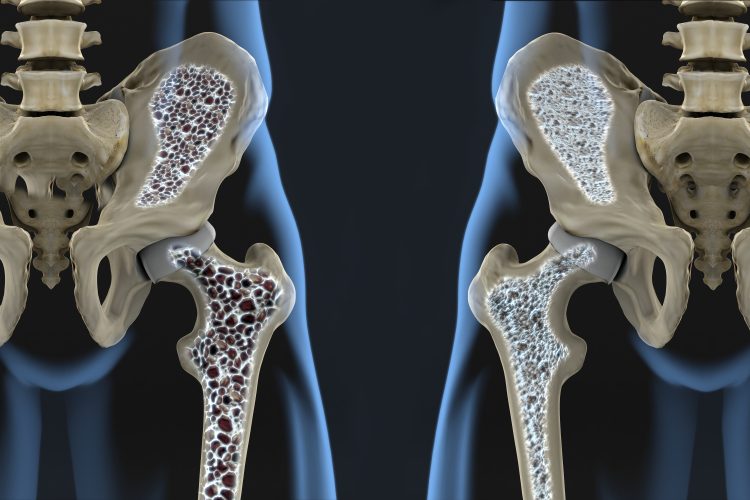
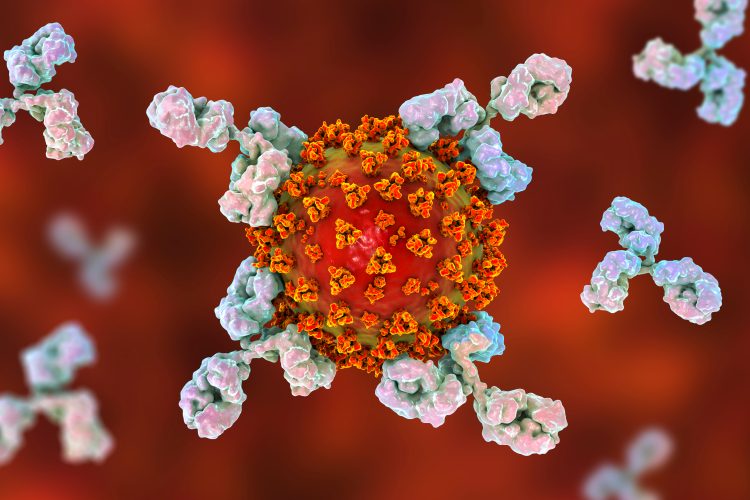
A label-free imaging technique for drug evaluation at single‑cell level
This article provides a brief overview of the technical and conceptual advantages of Raman spectroscopy, a label-free imaging technique that is being increasingly used for the purpose of drug evaluation.