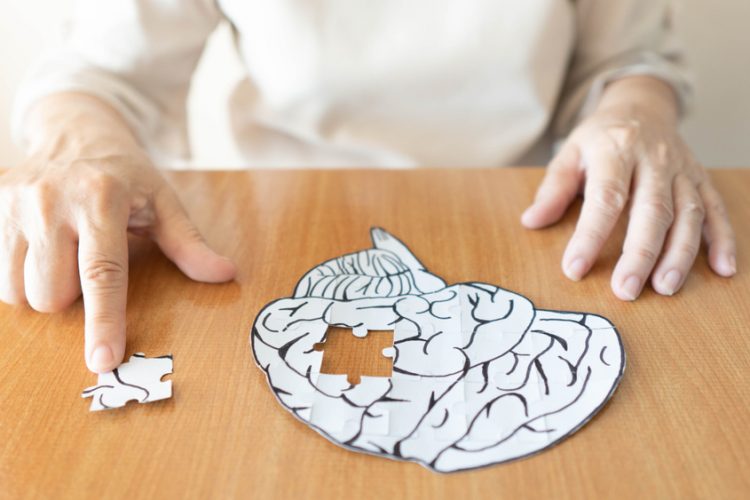
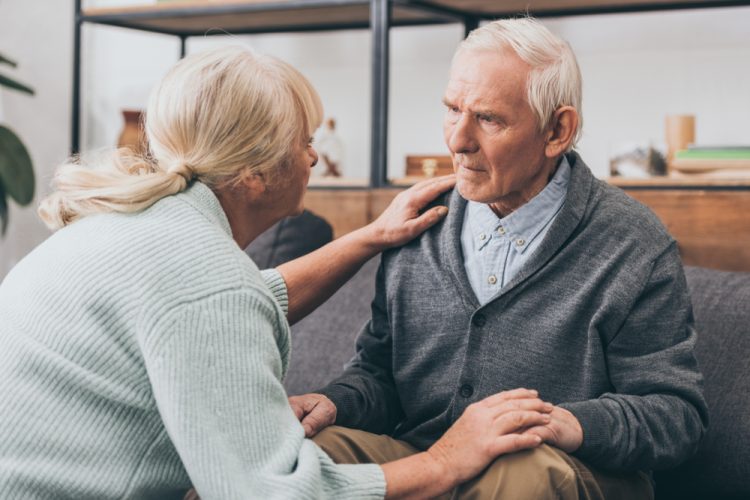
Drug Target Review – Issue 4 2021
This issue includes articles that discuss the development of long-term 3D tissue cultures from human biopsy samples, the application of flow cytometry in drug discovery and automation for upstream processing in a biologics manufacturing environment. Also included are features on informatics, proteomics and CRISPR.