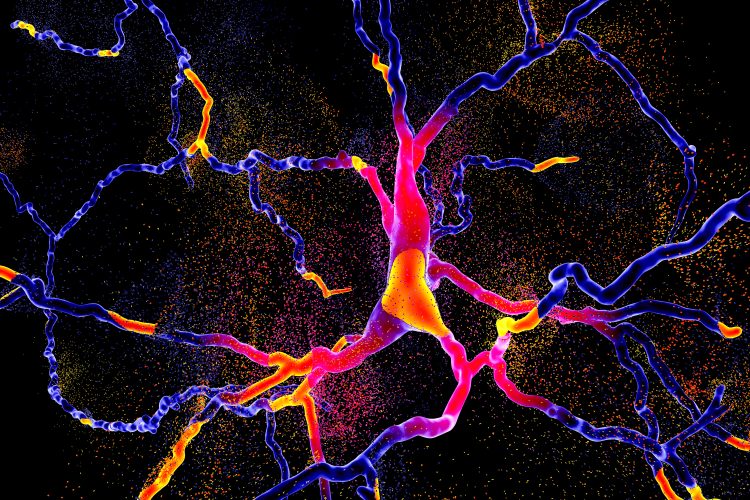
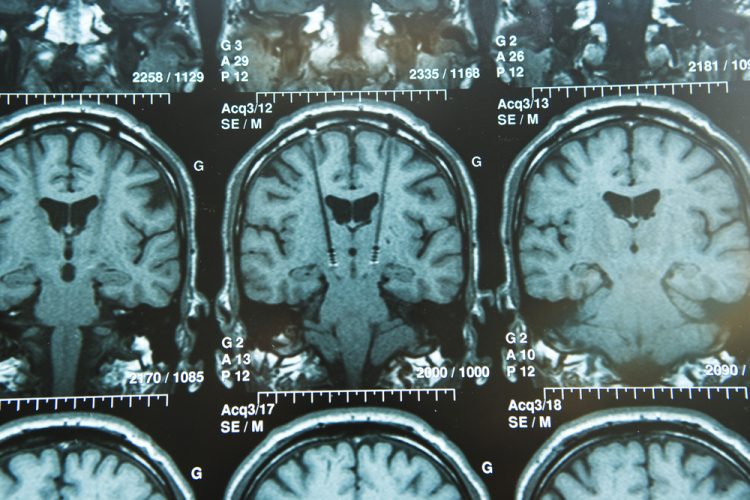
Delivering gene therapies to the brain to treat Alzheimer’s
Dr Ronald G Crystal, Professor and Chairman of the Department of Genetic Medicine, Weill Cornell Medical College, spoke to Drug Target Review’s Fraser Owen about his research into Alzheimer’s disease and why gene therapies represent a promising area of research for neurodegenerative conditions.