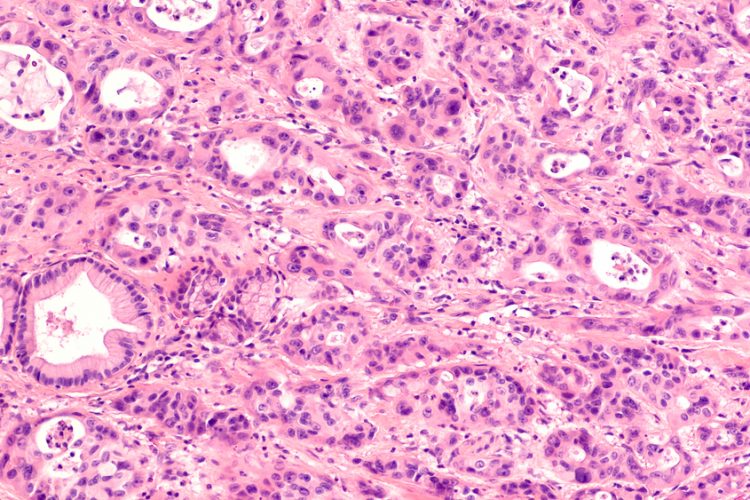
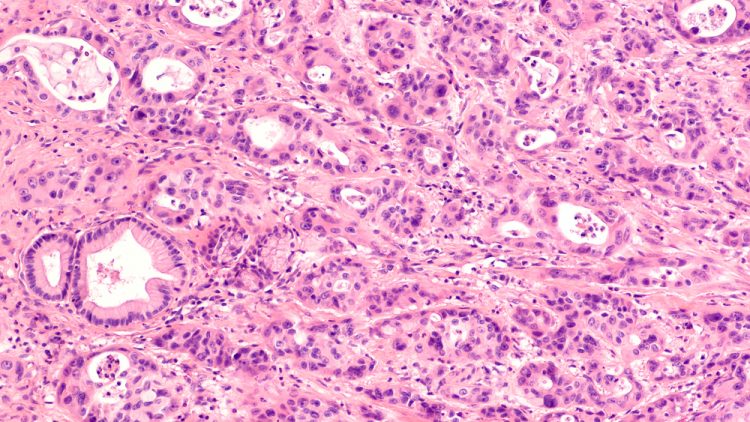
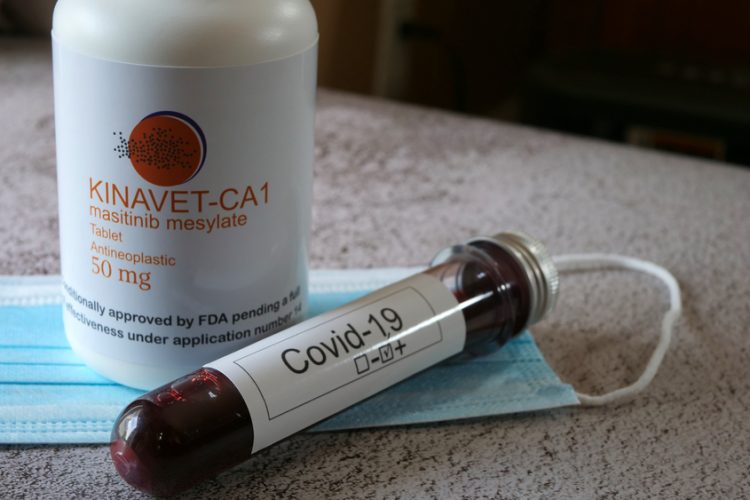
Exclusive report: AI & Informatics: Drug discovery and development
In this original report, find an in-depth analysis of AI and informatics within imaging, synthetic biology, drug screening and drug design. Featured interviews with experts from AstraZeneca, Auransa, PolarisQB and Chalmers University of Technology.