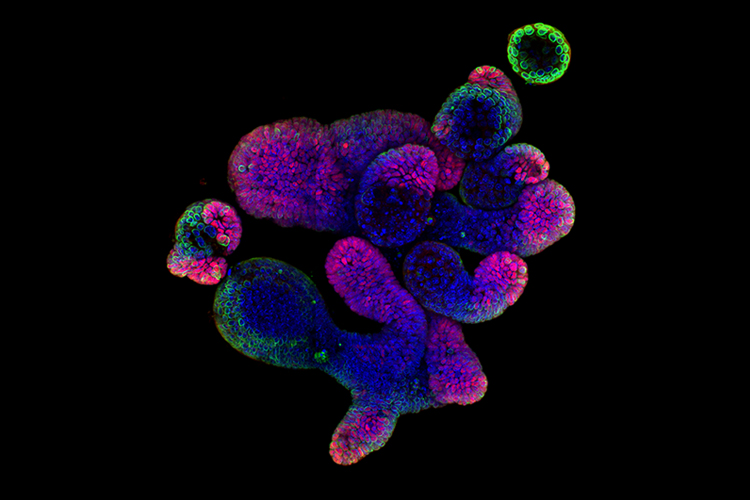
Application note: Evaluation of different ion-pairing reagents for LC/UV and LC/MS analysis of oligonucleotides
The effect of various ion pairing reagents (amines and acidic counterions) on the LC/UV and LC/MS analysis of oligonucleotides (ONs) has been studied.