Identifying a new target for metabolic liver disease treatment
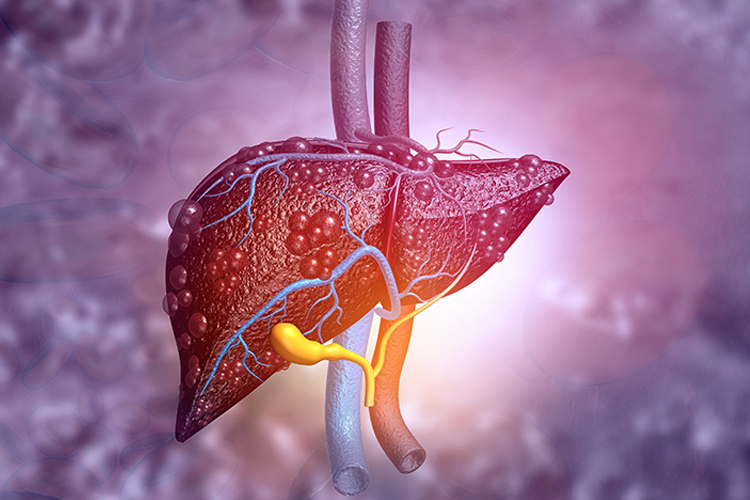
Scientists have identified protein tyrosine phosphatase delta (PTPRD) as a key regulator of liver metabolism, offering a potential new drug target for treating metabolic liver diseases like MASLD and MASH.