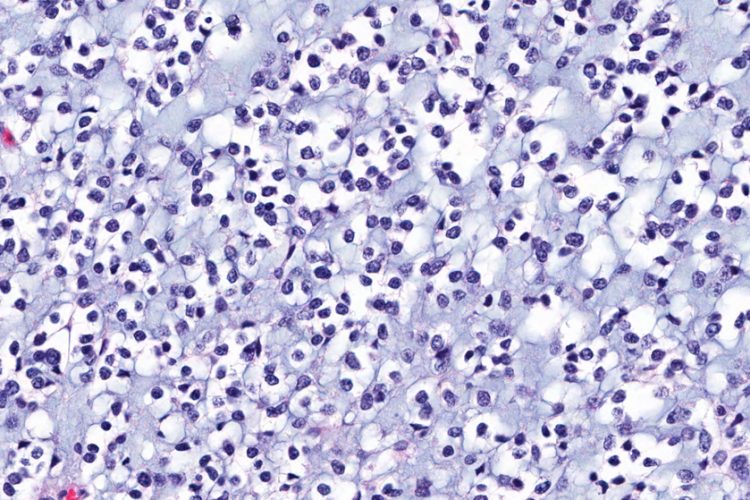
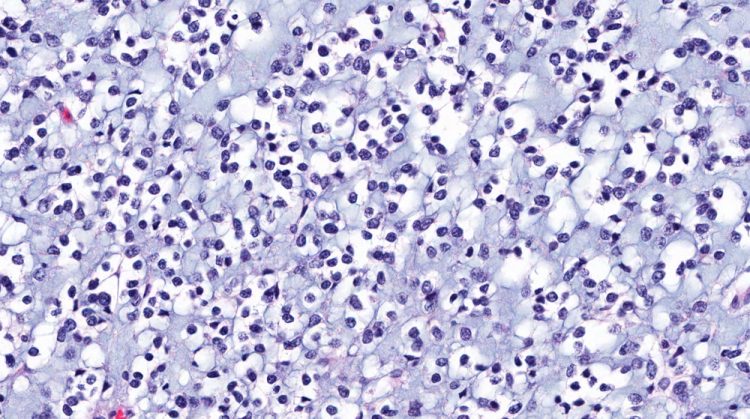
Peptides: a promising alternative to opioids for chronic pain relief
In an exclusive with Drug Target Review, researchers at the University at Buffalo explain how they developed a novel peptide that could be a future treatment for chronic inflammatory pain.