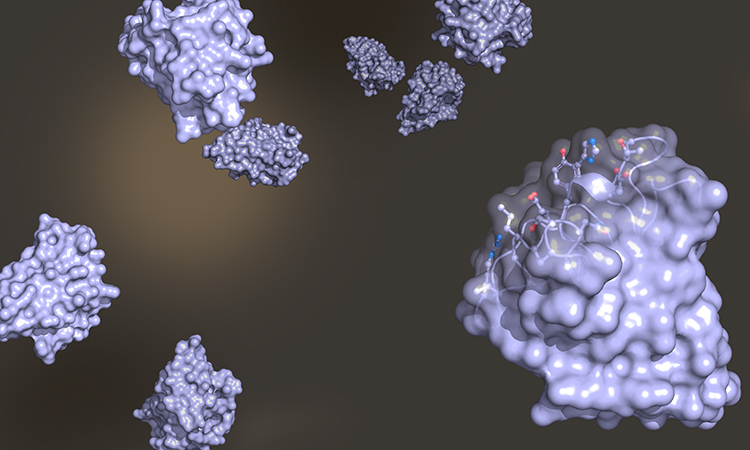
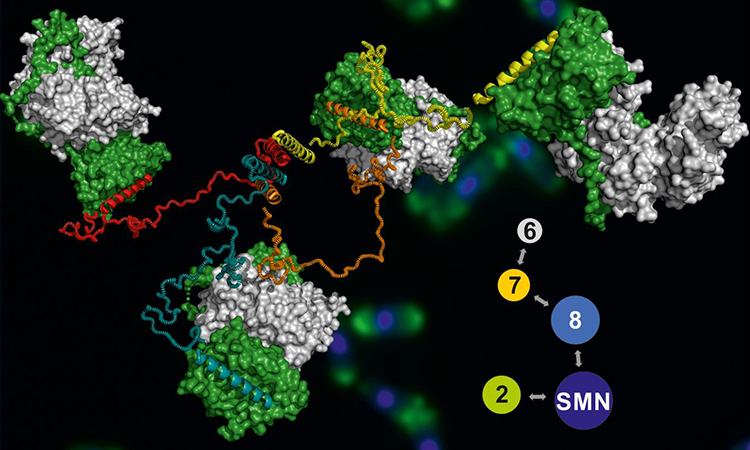
Determining the structure of nanobodies using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
Scientists at the New York University (NYU) Abu Dhabi have used nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) techniques to determine the structure of a specific nanobody, Nb23. Drug Target Review’s Victoria Rees spoke with lead researcher Professor Gennaro Esposito to find out how their findings could lead to a better understanding of…