Novel tuberculosis transport protein could be target of new treatments
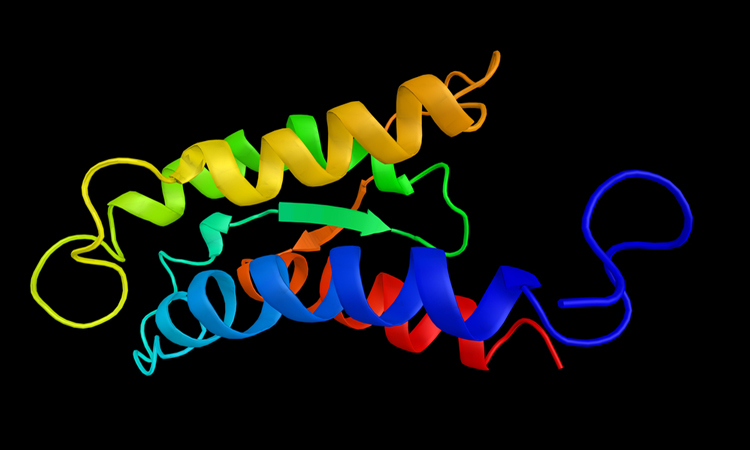
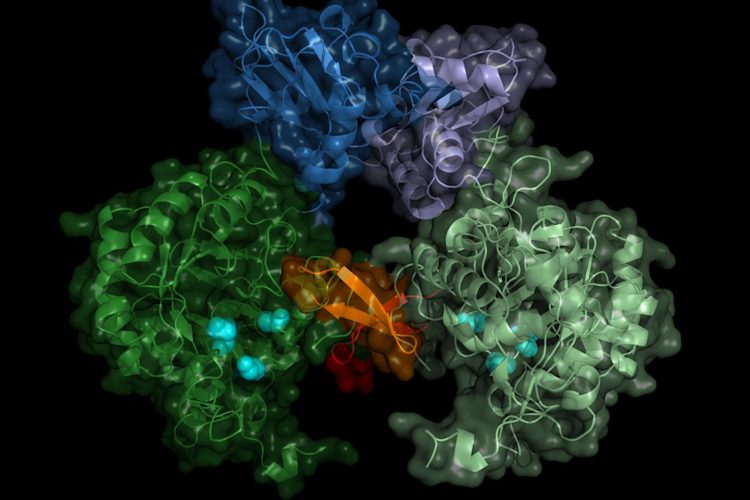
Cryogenic electron microscopy revealed that the vitamin B12 transporter on Mycobacterium tuberculosis acts like a non-selective sluice, transporting both the vitamin and antibiotics.