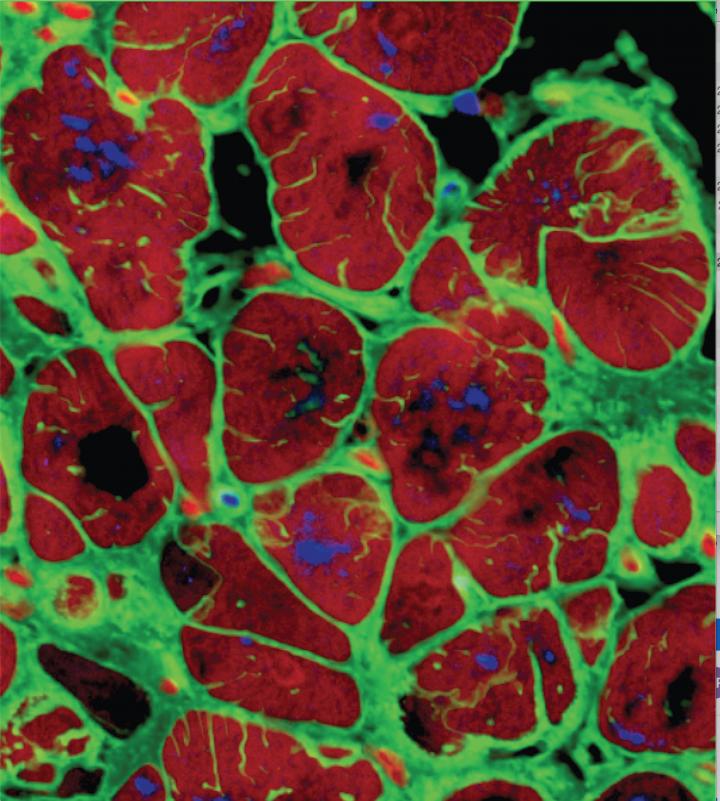
Restoring TERT to attenuate ageing hallmarks
In this Q&A, Dr Ronald DePinho of MD Anderson elucidates their preclinical proof-of-concept that adjusting TERT levels could be a viable therapeutic approach for mitigating age-related diseases, such as cancer, heart disease and Alzheimer’s.