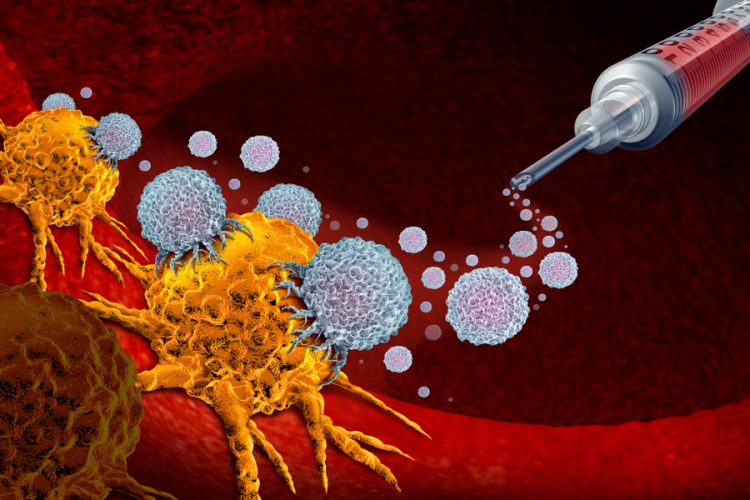
Gylden’s gold platform trains T cells to kill viruses
What if vaccines could train your immune system to eliminate infections at the source? Find out how Gylden Pharma’s gold nanoparticle platform delivers targeted T cell immunity - providing a precise and durable defence against complex infectious diseases.